ACETube® - dewatering system
Geotextile Bags, Tubes and Containers
About
Geotextile Tubes for Sludge Dewatering
ACETube® dewatering tubes are large, tubular containers made from high-strength, permeable geotextile fabric. They are essentially oversized sludge dewatering bags or geo-containers designed to filter water out of sludge and sediment, retaining the solid contents inside. The woven geotextile fabric has small pores that allow water (effluent) to pass through while trapping sludge materials, silt, sand, and other solid particles. These tubes (also known simply as geotextile tubes or dewatering filter tubes) can be fabricated in custom sizes and lengths to fit the needs of a particular site. This means you can have a tube made to virtually any length or circumference, which is useful for projects with limited space or irregular footprints. The high-strength woven geotextile construction enables the tube to hold large volumes of material without tearing, making it ideal for large-scale dewatering projects.
ACETube® dewatering tubes are engineered with polypropylene (PP) woven fabric that provides excellent tensile strength and filtration characteristics. They act as dewatering tubes that efficiently separate water from sludge. ACETube containers have multiple filling ports along their length for convenient slurry input, and they are manufactured to withstand the stresses of pumping and filling without rupturing. In short, geotextile dewatering tubes like ACETube® offer a robust containment solution for sludge that turns a liquid waste into a solid, manageable form.
Function
Containment
Protection
Filtration
Features
How Does the Dewatering Process Work?
The dewatering process using geotextile tubes is straightforward and highly efficient. First, the slurry of sludge or dredged material is pumped into the geotextile tube through one of its filling ports. This sludge may come from sources like municipal wastewater treatment plants, industrial processes, mining tailings, or dredging operations. Often a polymer flocculant is mixed into the sludge during pumping to help bind fine particles into larger aggregates, which enhances the dewatering process. As the tube fills up with the sludge, the water begins to drain out through the small openings in the geotextile fabric. The fabric acts as a filter: as water (now called filtrate or effluent) escapes, it leaves behind the heavier solids inside the tube. The released water is typically clear enough that it can be re-used or safely discharged into local waterways or treatment systems, making this an environmentally friendly process.
Filling a geotextile tube is usually done in cycles. A tube may be filled to a certain height (for example, a few feet of slurry) and then allowed to dewater for a period of time. During this time, gravity and the fabric’s filtration action will drain a large volume of water out of the tube. As the water dissipates, the solids settle and consolidate, creating space in the tube. Then another filling cycle can be performed, pumping more sludge in once again. These repeated fill-and-drain cycles continue until the tube is full of mostly solid material. Because the dewatering occurs gradually as the tube is loaded, the final solid content is high, typically over 99% of the solids are captured inside, with a greatly reduced moisture content. The end result is that what started as a high-volume liquid sludge is reduced to a much smaller volume of cake-like solid inside the tube.
After the final cycle and sufficient consolidation time, the remaining solids in the tube can be handled for disposal or reuse. At this stage, there are a few options. In some cases, the filled geotextile tube can be left in place for long-term storage or containment, for example, if it's a contaminated dredged sediment, the tube and its contents might be placed in a landfill or even left on site and capped if appropriate. Alternatively, the tube can be opened and the dewatered solids removed. Common practice is to cut open the top of the geotextile tube and then use equipment like a front-end loader or excavator to scoop out the dry solids and load them into a dump truck for transport. The solid material can then be disposed of in a landfill or in some cases applied to land (if the material is non-hazardous and meets regulatory approvals). The empty geotextile fabric can be disposed of or recycled as appropriate. Throughout this entire dewatering process, no complicated machinery (like filter presses or centrifuges) is required, just a pump to fill the tube and time for gravity and filtration to do the work. This simplicity is a key to why geotextile tube dewatering is so cost-effective and efficient.
High Capacity, Custom Sizes, and Durable Fabric
ACETube® dewatering tubes are designed to handle large volumes of sludge in a single container, making them well-suited for large-scale projects. ACETube® dewatering tubes, for instance, are made of high-strength polypropylene woven geotextiles with robust tensile and seam strength. This means each tube can hold a huge quantity of sludge without bursting. The capacity of a tube is essentially determined by its dimensions, tubes can be manufactured in diameters of multiple meters, and the length of a tube is limited only by practical handling and site space (they are often delivered folded or on a roll). Because the geotextile tubes can be fabricated to custom lengths and circumferences, an engineer can specify a tube size that maximizes the use of the available footprint on site. If space is constrained, tubes can even be stacked in layers after they are filled (with proper precautions) to increase the amount of sludge that can be processed in the same area.
The woven geotextile fabric used in these dewatering tubes is carefully engineered for the task. It has an optimal aperture size (pore size) that achieves a balance between permeability and retention: it’s small enough to retain even fine particles and fines within the tube, but large enough to allow water to pass through quickly. This gives a high solid retention rate while still allowing efficient dewatering. The fabric is typically a strong synthetic material (like polypropylene or polyester) that is resistant to degradation. ACETube® geotextile tubes, offer excellent durability, they resist abrasion from the sludge, ultraviolet sunlight exposure, chemical degradation from acidic or alkaline contents, and biodegradation. These properties are important because dewatering projects often take place outdoors under harsh conditions, and the tubes may need to sit for weeks or months while dewatering and consolidating the material. The durability ensures the tube will not tear or fail during filling, and it can withstand exposure to the elements for extended periods. In fact, quality geotextile containers are known to maintain integrity for years if needed for long-term storage. Manufacturers like ACE Geosynthetics adhere to strict quality control (ACETube® products are produced under ISO 9001 certified processes) to ensure each tube performs reliably in the field.
Another advantage is that geotextile tubes can be customized not only in size but also in fabric properties. Depending on the type of sludge and whether chemical conditioning (polymers) is used, the fabric's weave and coating can be selected to achieve specific filtration performance. For instance, a certain weave pattern might provide better retention of very fine clay particles, while another might maximize flow rate for coarser materials. This customization means you get an optimized dewatering system for your particular sludge characteristics, which improves overall efficiency.
Advantages Over Traditional Dewatering Methods
Using geotextile dewatering tubes for sludge management offers several significant advantages compared to traditional methods of sludge dewatering or disposal. One of the primary benefits is cost savings. Geotextile tubes are widely regarded as a cost-effective alternative to methods such as sludge lagoons, sand drying beds, belt filter presses, centrifuges, or hauling liquid sludge off-site. The operation of a geotextile tube system is relatively low-tech and low-energy, aside from the pump that fills the tube, there is no need for electricity to power large machinery, which reduces energy costs and equipment costs. In fact, dewatering with passive filtration requires far less energy than mechanical dewatering, translating into lower project operating costs.
Because the water is drained and filtered out passively, project costs are further reduced by minimizing the volume that needs to be transported or treated afterwards. For example, instead of paying to haul away many tanker trucks of liquid sludge, a contractor can dewater on site and then only transport the consolidated solids (which might be a small fraction of the original volume). This also means fewer trips and less fuel, contributing to both cost savings and reduced carbon emissions.
Geotextile tubes also have a much smaller footprint and more flexibility in placement than some traditional methods. They do not require building large infrastructures (like constructing dewatering pits or permanent facilities). A tube can be laid out on any reasonably flat area at the project site. This is especially useful when space is limited or the dewatering operation needs to be near where the sludge is generated (e.g., alongside a dredging operation or at a wastewater plant with little free land). Since they dewater faster than letting sludge sit in open-air pits or lagoons, and since you can stack or arrange tubes efficiently, they optimize land usage and allow dewatering in areas that might otherwise not accommodate such operations.
Environmentally, geotextile dewatering is often a better choice. The filtered water filtrate that comes out of the tubes is usually clean enough that it can be returned to the environment or reused, which helps conserve water resources. The process does not involve chemicals beyond optional flocculants, and it produces no toxic byproducts, it’s essentially just separating existing solids from water. By avoiding the need to truck liquid waste long distances, it cuts down on fuel usage and emissions making it a more environmentally friendly and sustainable solution. Furthermore, because the solids are well-contained in the geotextile, there is little risk of spillage or contamination of the site during dewatering, unlike open pits which could overflow or leak. In many cases, the use of geotextile tubes has been shown to have minimal environmental impact while achieving effective dewatering, aligning with green project goals.
Applications of Sludge Dewatering Tubes
ACETube® geotextile dewatering tubes have a wide range of applications wherever there is a need to separate water from solid sludge or sediment. Some common applications include:
-
Municipal wastewater treatment sludge – Wastewater treatment plants produce biosludge that needs dewatering. Geotextile tubes can be used on-site at municipal facilities to dewater sewage sludge, eliminating the need for large drying beds or excessive hauling. The tubes efficiently consolidate the sludge, which can then be transported as a solid cake for disposal or further treatment.
-
Industrial process sludge – Many industries generate sludge from processes such as pulp and paper manufacturing, food and beverage processing, or chemical production. Geotextile tubes can handle fine-grained, inorganic industrial sludges as well as organic sludges. They are chemical-resistant, so they can even be used for certain hazardous or contaminated sludges (with proper handling and liners) to trap contaminants safely.
-
Mining tailings and mineral processing – Mining operations often have large volumes of tailings slurry or sludge from mineral processing. Instead of building tailings ponds or using large presses, mines can pump the tailings into huge dewatering tubes. The tubes will retain the solid particles (like fine silt, clay, and sand from the tailings) and release water that can often be recirculated in the process. This is an efficient way to reduce the water content in tailings and reclaim water.
-
Dredged material and sediment removal – Perhaps one of the most common uses of dewatering tubes is in dredging projects. When rivers, lakes, harbors, or canals are dredged, the wet sediment slurry can be pumped into geotextile tubes on the shore. This captures the dredged materials (sand, silt, contaminated sediment, etc.) inside the tubes. The water drains out and is often returned to the water body, while the sediment is left in the tubes to consolidate. These tubes full of dredged sediment can then be transported if needed, or even left in place to form structures (for example, sometimes dewatered dredge tubes are used to create berms). For environmental dredging (cleaning contaminated sediments), tubes are very effective at dewatering and isolating the pollutants in a manageable form.
-
Agricultural waste and animal manure – Farms and livestock operations can produce significant liquid waste (manure lagoons, etc.). Geotextile dewatering bags and tubes are used to treat these by pumping the nutrient-rich slurry into tubes. The water that drains out can often be reused for irrigation since it will contain much fewer solids, while the captured solids (rich in nutrients) can sometimes be used as fertilizer or at least disposed of more easily once dried.
-
Construction and stormwater projects – On construction sites, stormwater or runoff can carry sediment that needs to be removed before discharge. Small geotextile dewatering bags or tube systems can be deployed to filter out sediment from pump-out water (for example, from excavations or cofferdams). They serve as portable, easy-to-use filters that prevent silts from polluting nearby water bodies.
In all these applications, ACETube® dewatering tubes can be employed, and they can be tailored to the specific project needs. ACE Geosynthetics offers technical support to help with system design, tube selection, and even the dewatering operation itself, ensuring that the geotextile tube dewatering system works optimally for the given material and site conditions. After more than 15 years in geotextile manufacturing, the ACETube® line has accumulated extensive experience in diverse projects, from municipal sludge treatment to large-scale dredging operations. This means their team can advise on the right tube fabric, size, filling strategy, and any polymer usage to achieve the best results for a given project.
Conclusion
Geotextile dewatering tubes have revolutionized the way sludge and slurry materials are handled by providing a simple, efficient, and low-cost dewatering solution. These dewatering tubes (large filter fabric containers) turn a messy liquid sludge into a solid that is easy to manage, reducing both the volume and the hassle of disposal. They achieve high rates of solid capture and volume reduction without the need for complex infrastructure, and they excel in scenarios where traditional methods might be too expensive or impractical. The ACETube® dewatering system engineers and project managers can significantly cut down project costs, expedite the dewatering timeline, and minimize environmental impact compared to older methods.
In summary, sludge dewatering tubes like ACETube® offer an engineered, technical solution to sludge management that is both practical and sustainable. Whether for a wastewater plant looking to improve its sludge handling, a dredging project needing to process sediment, or any situation where water needs to be separated from solids, geotextile dewatering tubes provide a reliable answer. They embody a combination of high capacity, strength, and efficiency that is hard to beat. As more industries and municipalities seek cost-effective and environmentally friendly practices, geotextile dewatering tubes are likely to remain a cornerstone technology for years to come, continuing to save time, save money, and simplify sludge management tasks.
• Excellent filtration characteristics to enhance processing efficiency• Highly customized solutions provided for best cost-effectiveness
• Easy installation and few additional facilities needed to save time and costs
• Environmentally friendly with less carbon emission
Resources
-
【Brochures】ACETube® Product Brochure
-
【Brochures】2024 CASE STUDY COLLECTION
-
【Brochures】 ACETube® - Dewatering System Product Brochure
-
【Brochures】ACE Solutions with ACE Products:ACEGrid®, ACETex®, ACETube®
-
【Brochures】An Overview of ACEGrid®, ACETex®, and ACETube®
-
【Brochures】Case Study Collection-Safety and Reliability with ACE Solutions
-
【Brochures】ACE Solutions in Hydraulic Engineering
-
【Data Sheets】ACETube® Geotextile Tube TDS
-
【Installation Guidelines】Installation Guideline for ACETube® Sludge Dewatering (Member Only)
-
【Papers】Industrial Sludge Dewatering Using Geotextile Tubes
-
【Others】Case Study Collection- Environmental Protection
-
【Videos】ACETube® (Geotextile Tube) Dewatering System on Sediment Dredging
-
【Videos】ACETube® Application - Dewatering System on Sludge Dredging
-
【Videos】ACETube® Application - Industrial Wastewater Treatment
-
【Videos】ACETube® (Geotextile Tube) Pressurized Pillow Bag Test
-
【Videos】How to Dewater Sludge by Using ACETube® (Geotextile Tube) Dewatering System?
-
ACETube® - Dewatering System Product Brochure
-
ACETube® Product Brochure
-
ACETube® Geotextile Tube TDS
-
Installation Guideline for ACETube® Sludge Dewatering (Member Only)
-
Industrial Sludge Dewatering Using Geotextile Tubes
Related Case Studies
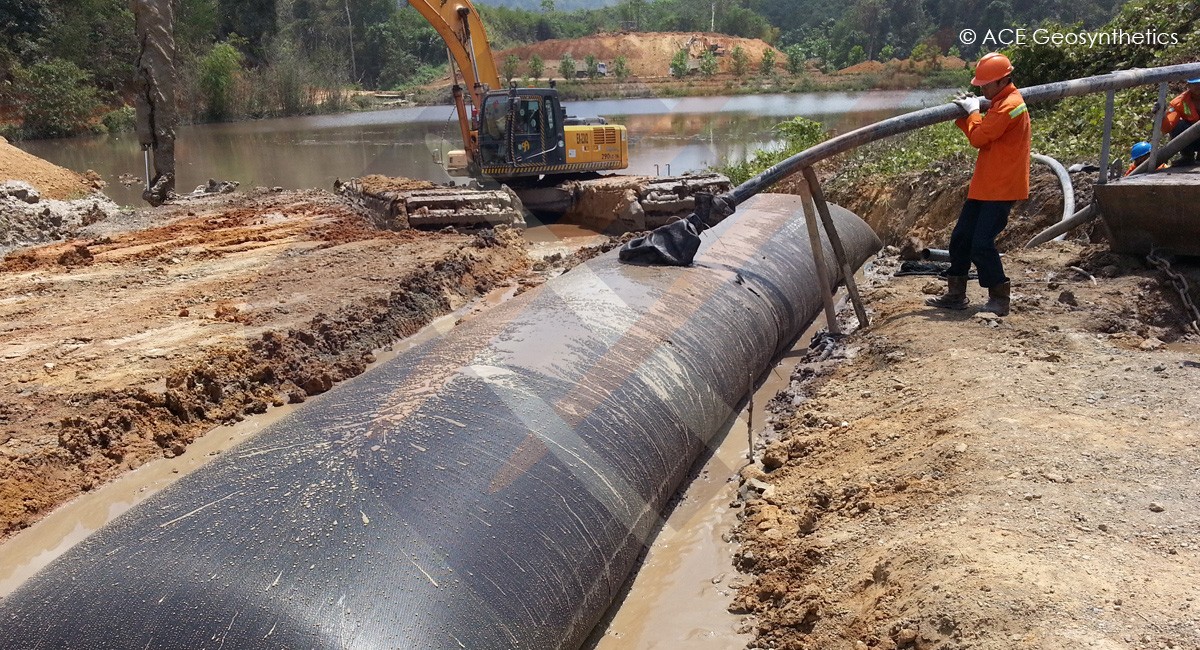

Use Geotextile Tube as Mine Slurry Dewatering Treatment, Indonesia
Application:Sludge Treatment, Tailing Dewatering

Sludge Dewatering in a Sewage Treatment Plant, Lithuania
Application:Sludge Treatment
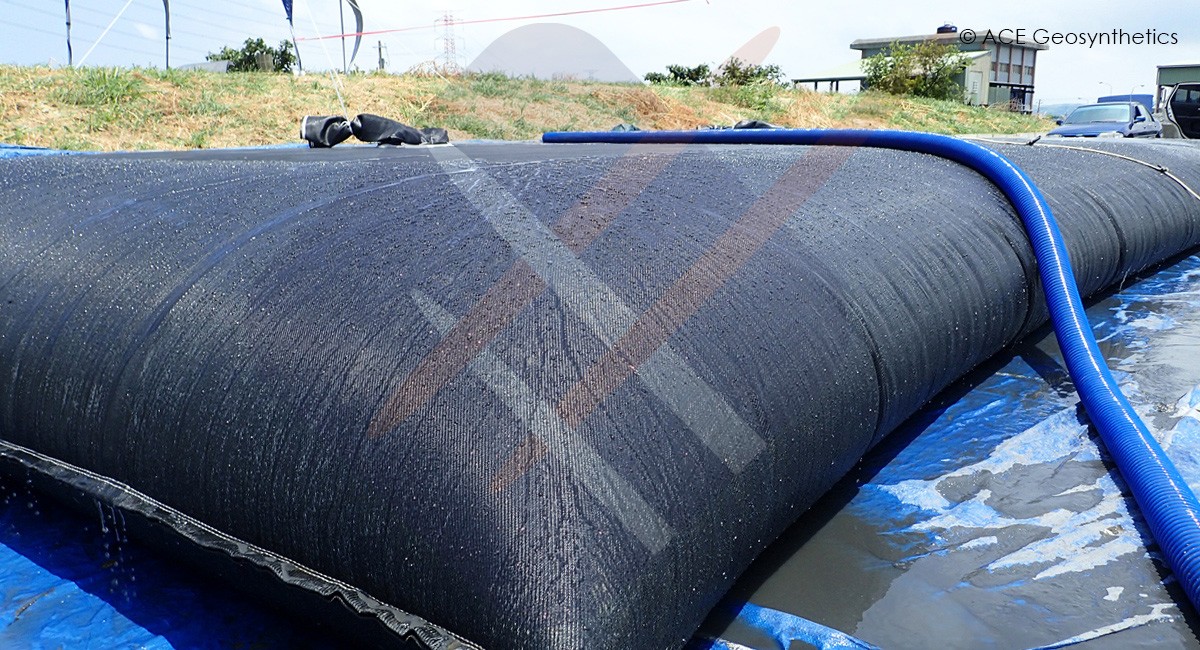

Sewage and Sludge Dewatering Treatment in the Chuansing Industial park, Taiwan
Application:Sludge Treatment







